髒水與排泄物橫流,50 萬羅興亞難民面臨傳染病危機/無國界醫生孟加拉現場
文/無國界醫生
國際醫療人道組織無國界醫生指出,
無國界醫生自 1985 年起於孟加拉工作,目前在科克斯巴扎爾區(
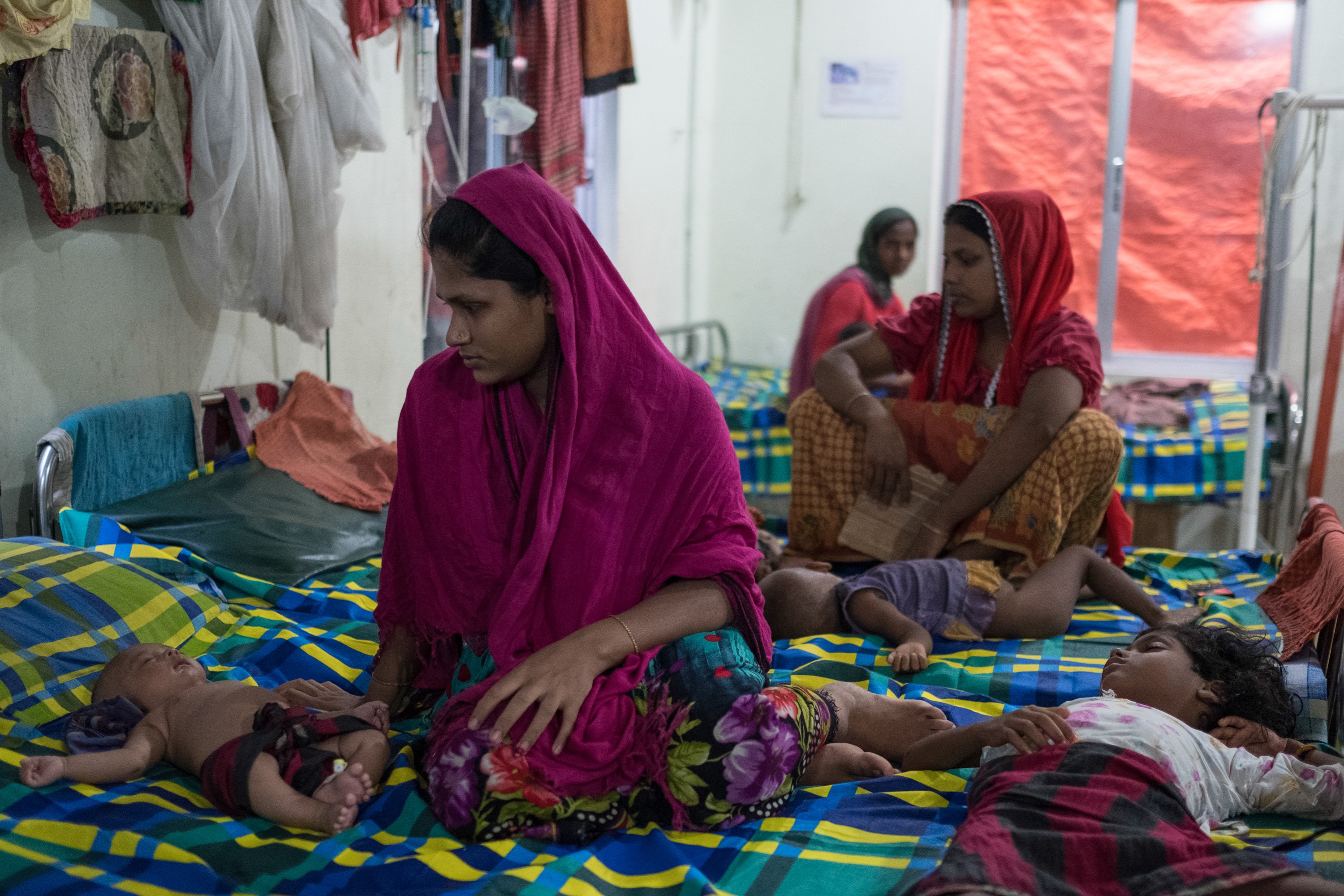

營地居住環境惡劣,並缺少飲用水和糧食供應,無國界醫生在營地附件設立診所,每天都接收大批病人/©Antonio Faccilongo
在針對羅興亞人的暴力行動展開以來,
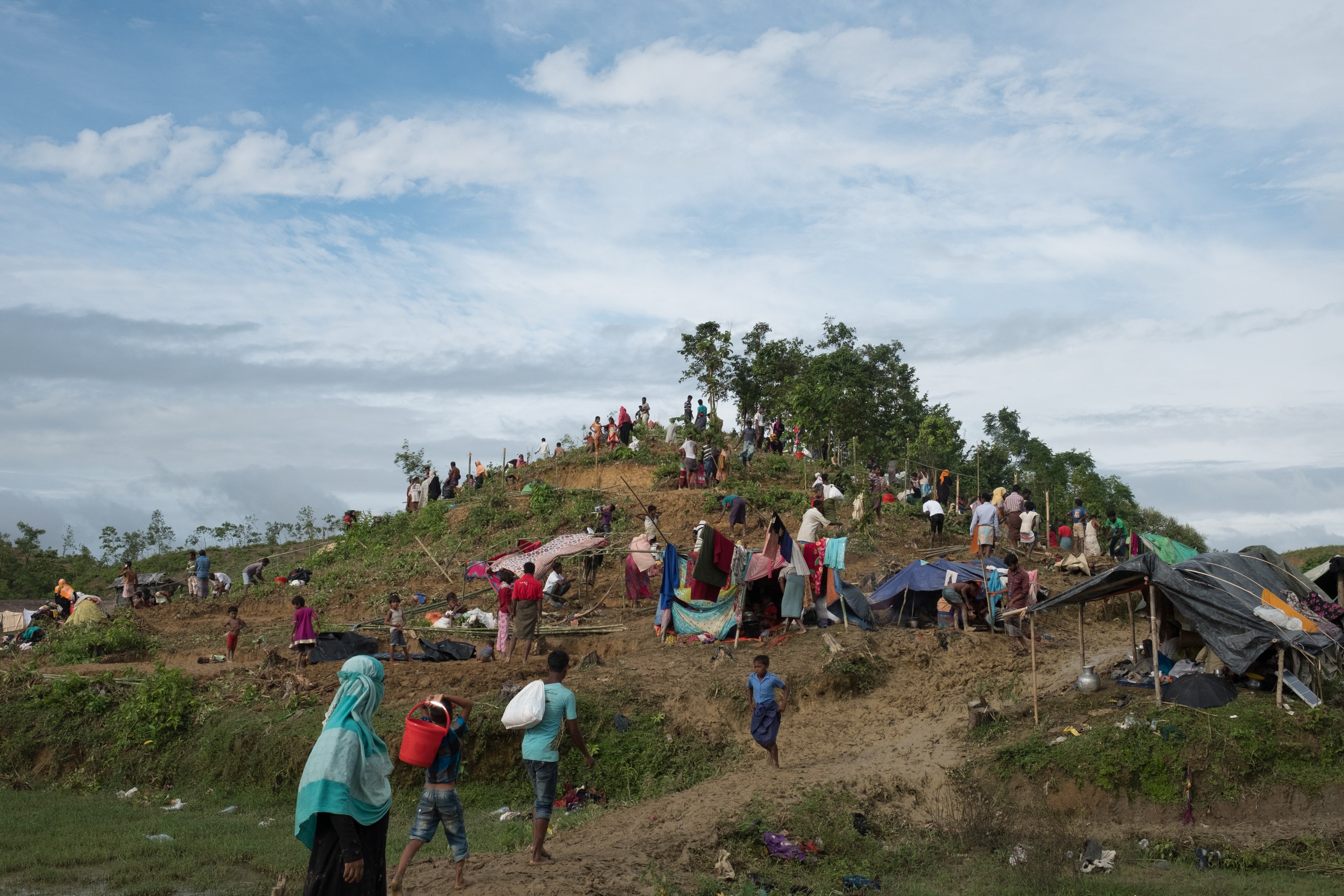
大部分剛抵達的難民落腳於臨時營地,沒有適當的棲身之所、糧食、
無國界醫生緊急醫療項目統籌懷特(Kate White)說:「這些聚居地就在貫穿該區的一條二線道馬路兩旁,

營地環境惡劣,但每天仍有大批難民湧至。/©Antonio Faccilongo
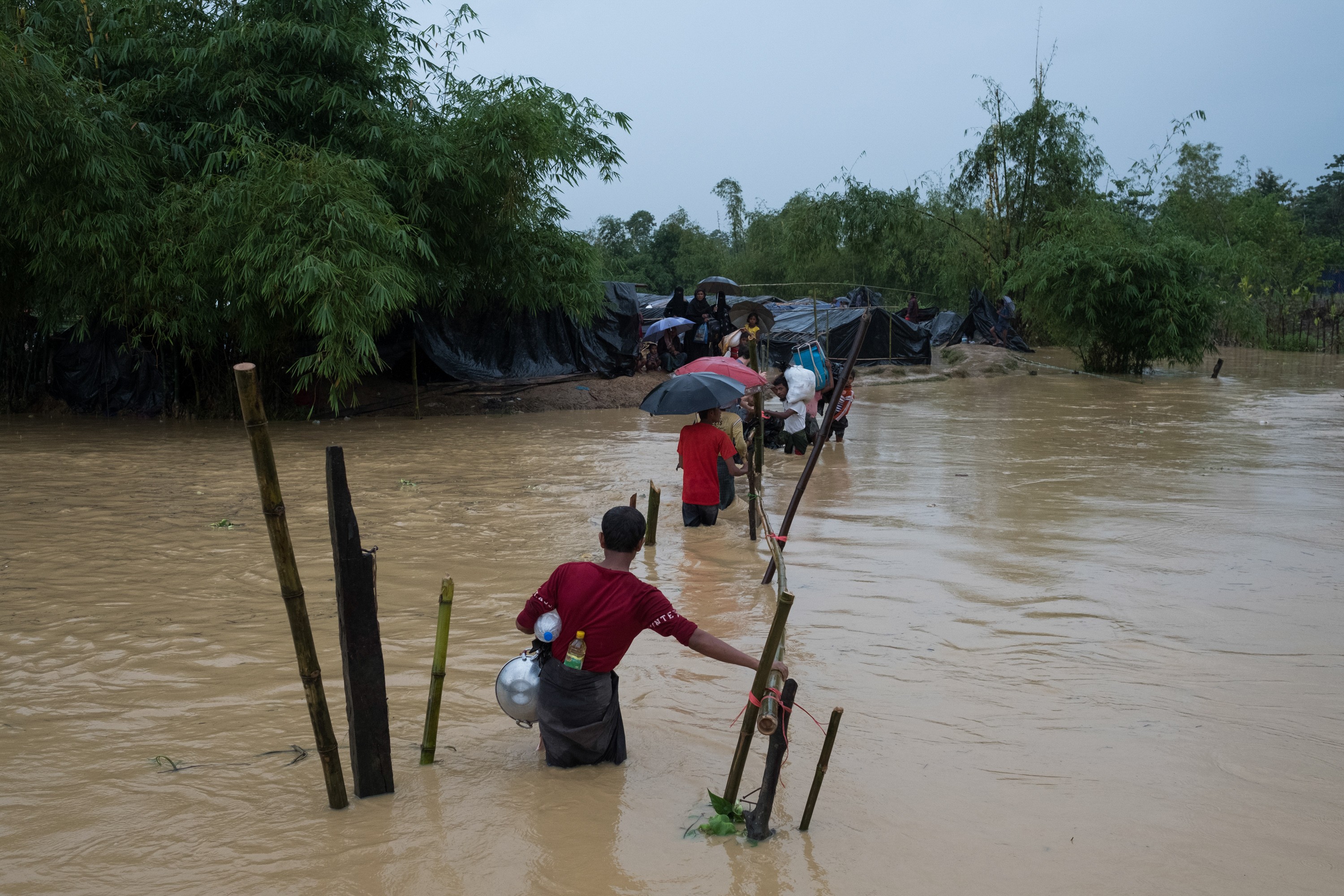
在幾乎沒有飲用水的情況下,人們從稻田、水坑或在雙手被排泄物汙染的情況下挖掘淺井取水飲用。自 9 月 6 日至 17 日間,
在聚居地及其周邊地區,糧食安全非常脆弱。新到的難民完全依賴人道援助,糧食的市場價格暴漲,
包括無國界醫生診所在內的所有醫療設施,都完全不堪重負。
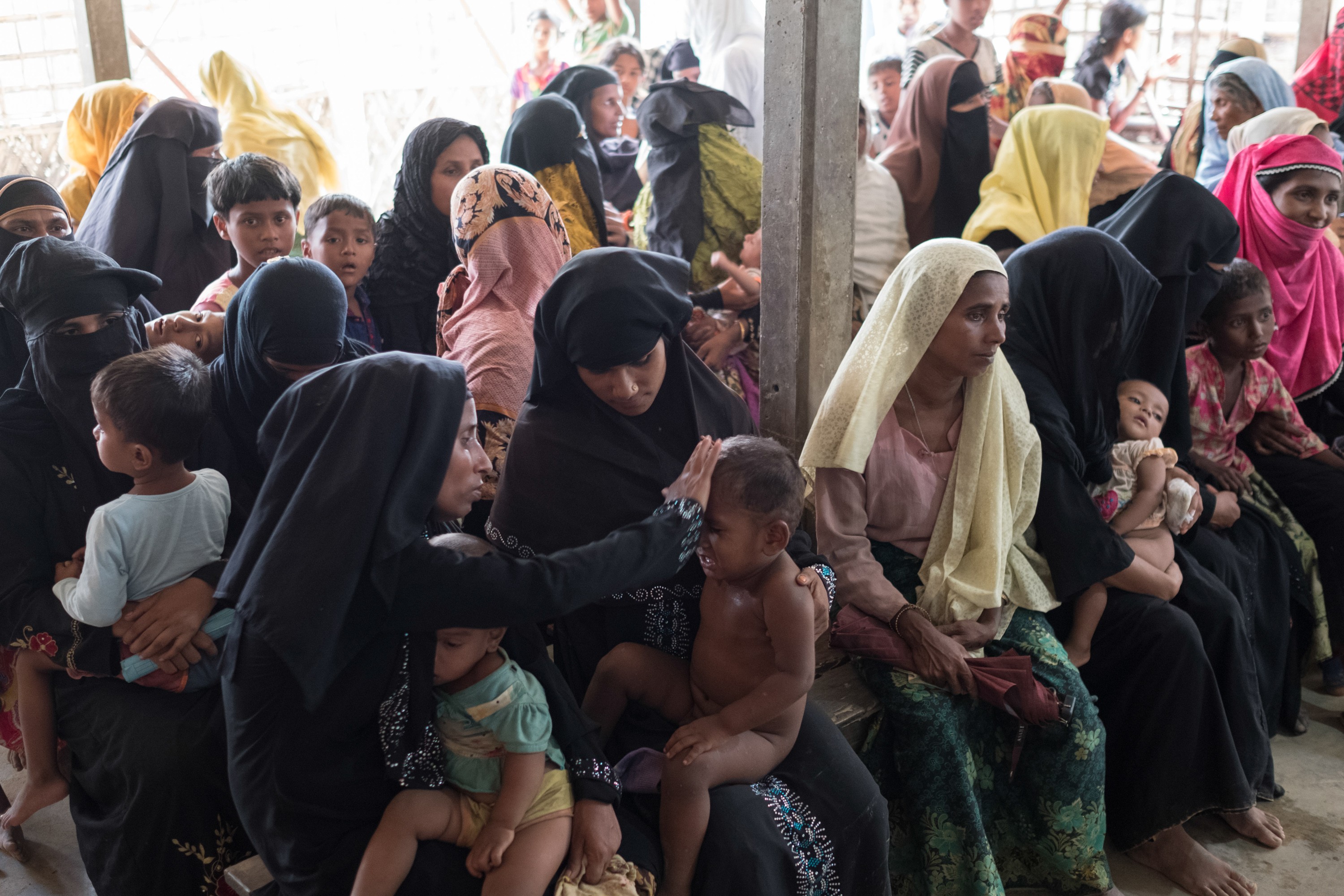

每天在無國界醫生診所外等待門診的病人/©Antonio Faccilongo
鑒於巨大及快速增長的人數,
奧納斯說︰「數以十萬計的難民目前正處於極度危困的處境,
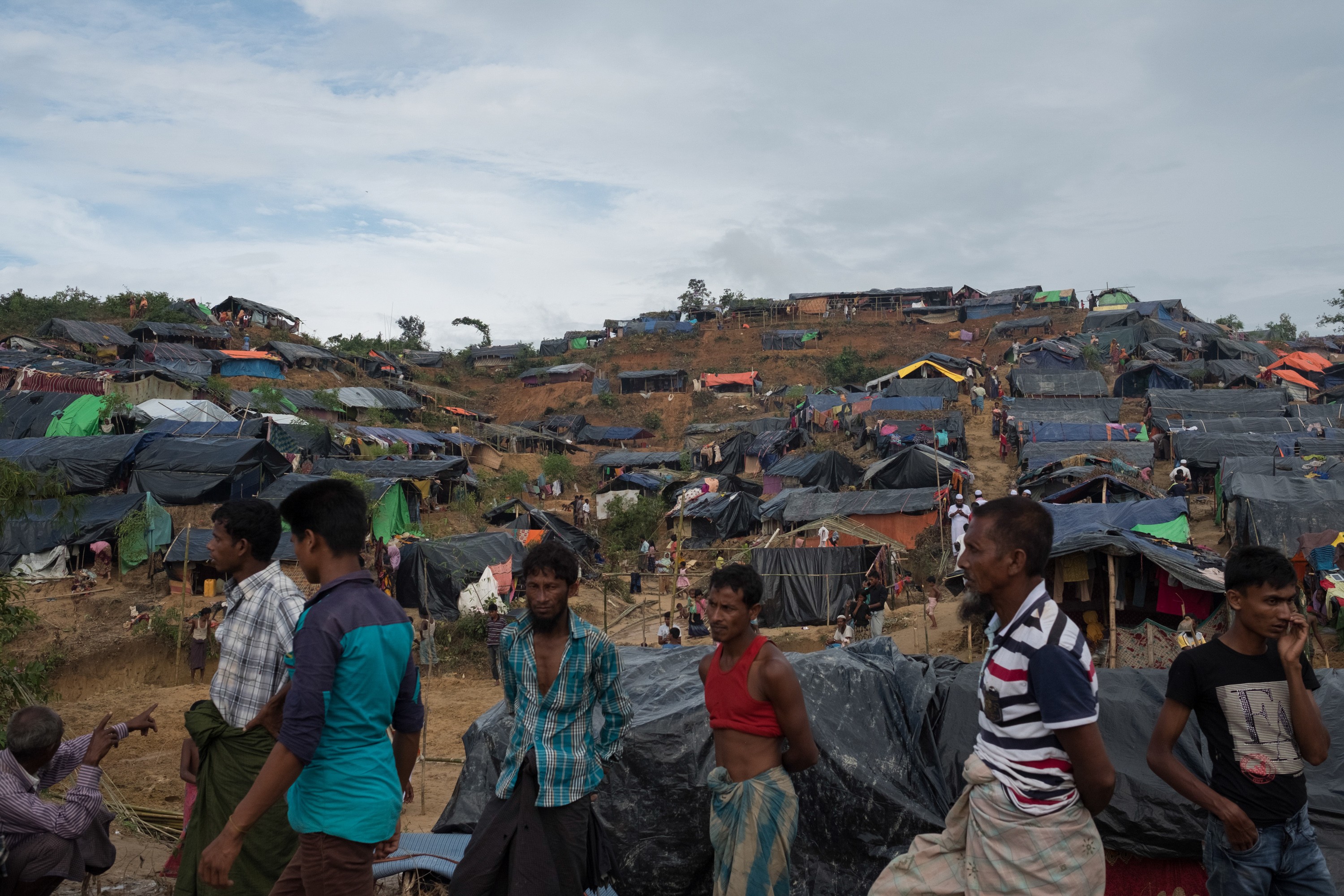

大批難民湧至,臨時營地佈滿山頭/©Antonio Faccilongo
延伸閱讀:
【羅興亞危機】「即刻停止種族清洗」 孟加拉總理 UN 大會提 5 點建議
翁山蘇姬 9 月 19 日針對羅興亞難民事件全國演說全文(英文版)
Bangladesh:Immediate action needed to avert massive public health disaster
A massive scale-up of humanitarian aid in Bangladesh is needed to avoid a massive public health disaster following the arrival of hundreds of thousands of Rohingya refugees, says the international medical humanitarian organization Médecins Sans Frontières/Doctors Without Borders (MSF).
Following a wave of targeted violence against Rohingyas more than 422,000 people have fled to Bangladesh from Rakhine State in Myanmar within a three week period. The most recent influx of Rohingya refugees has added to the hundreds of thousands of Rohingyas who fled across the border during episodes of violence in previous years.
Most of the newly arrived refugees have moved into makeshift settlements without adequate access to shelter, food, clean water, or latrines. Two of the main pre-existing settlements in Kutupalong and Balukhali have effectively merged into one densely populated mega-settlement of nearly 500,000 refugees, making it one of the largest refugee concentrations in the world.

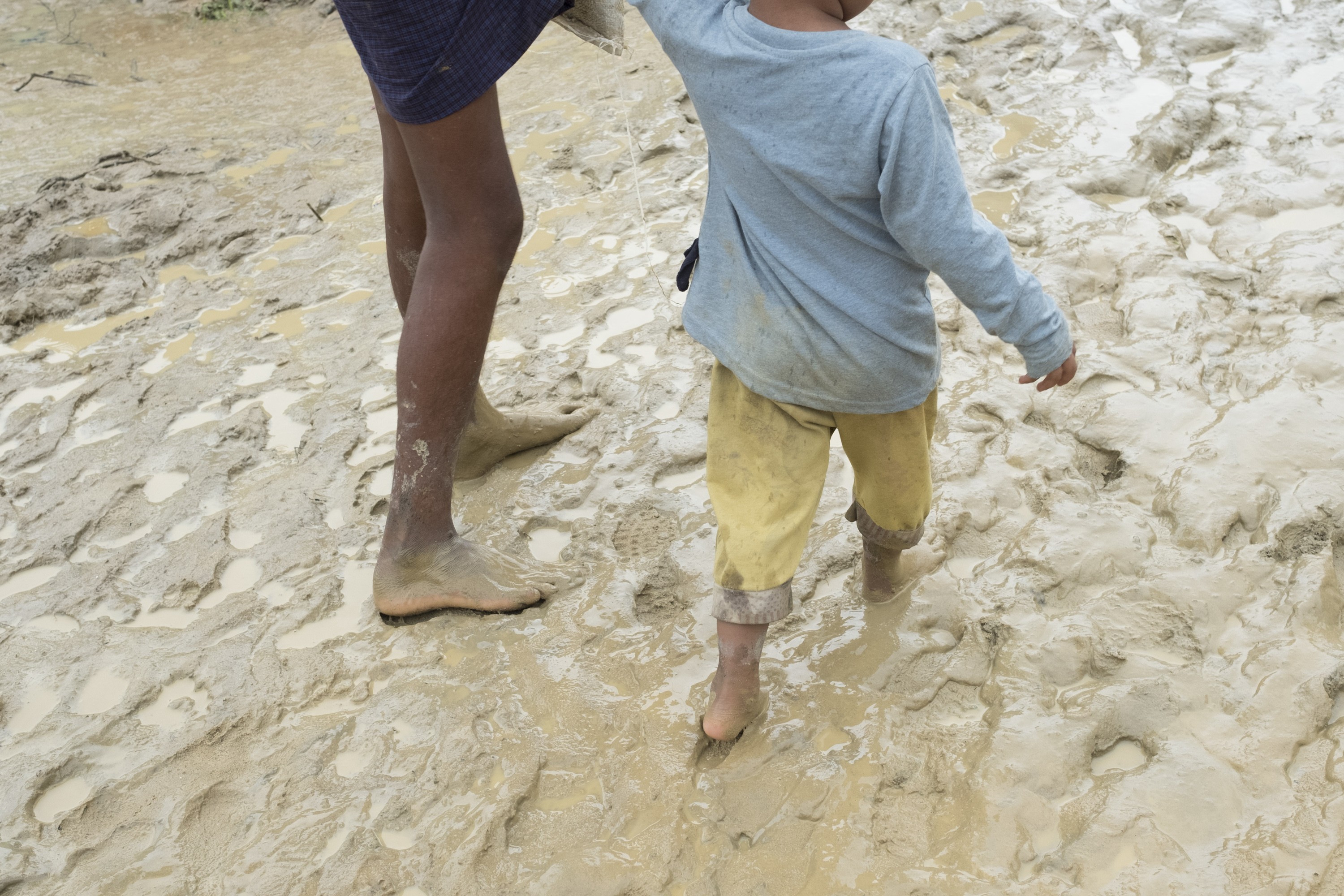
難民身無長物,僅能以塑膠帆布和樹枝搭建臨時帳篷,飽受風吹雨打/©Antonio Faccilongo
“These settlements are essentially rural slums that have been built on the side of the only two-lane road that runs through this part of the district,” says Kate White, MSF’s emergency medical coordinator. “There are no roads in or out of the settlement, making aid delivery very difficult. The terrain is hilly and prone to landslides, and there is a complete absence of latrines. When you walk through the settlement, you have to wade through streams of dirty water and human faeces.”
With little potable water available, people are drinking water collected from paddy fields, puddles, or hand-dug shallow wells which are often contaminated with excreta. At MSF’s medical facility in Kutupalong, 487 patients were treated for diarrhoeal diseases between 6 and 17 September. “We are receiving adults every day on the cusp of dying from dehydration,” says White. “That’s very rare among adults, and signals that a public health emergency could be just around the corner.”
Food security in and around the settlements is incredibly fragile: newly arrived refugees are completely reliant on humanitarian aid, prices in the market are skyrocketing and the lack of roads is compromising access to the most vulnerable populations. “With very little money and chaotic, congested and insufficient food distributions, many Rohingya are only eating one meal of plain rice per day,” says White. “Some refugees told us that after days without food all they had eaten was one bowl of rice they received from a Bangladeshi restaurant owner, shared among a family of six.”

營地環境惡劣,但每天仍有大批難民湧至/©Antonio Faccilongo
Meanwhile, medical facilities, including MSF’s own clinics, are completely overwhelmed. Between 25 August and 17 September, MSF clinics received a total of 9,602 outpatients, 3,344 emergency room patients, 427 inpatients, 225 patients with violence-related injuries, and 23 cases of sexual violence.
There is a very high risk of an infectious disease outbreak in the area given the huge and rapid increase in the population, as well as the known low vaccination coverage among the Rohingya community in Myanmar. Comprehensive vaccination campaigns for measles and cholera need to be launched immediately to reduce the outbreak risk and protect the Rohingya and Bangladeshi populations. In anticipation, MSF has prepared an isolation unit in the Kutupalong medical facility to rapidly contain any suspected or identified cholera or measles cases. “The situation in the camps is so incredibly fragile, especially with regard to shelter, food and water and sanitation, that one small event could lead to an outbreak that may be the tipping point between a crisis and a catastrophe,” says Robert Onus, MSF Emergency Coordinator.
“Hundreds of thousands of refugees are living in an extremely precarious situation, and all the preconditions for a public health disaster are there,” adds Onus. “We most likely still haven’t seen the full impact of this crisis in terms of health. There is an acute need for a massive humanitarian intervention focusing on food, clean water, shelter, and sanitation, and a solution is needed to reduce the size of these massive, congested camps.”
營地居住環境惡劣,缺乏飲用水和糧食供應,無國界醫生在營地附近設立診所,每天接收大批病人/©Antonio Faccilongo
MSF in Bangladesh
MSF first worked in Bangladesh in 1985. Close to the Kutupalong makeshift settlement in Cox’s Bazar district, MSF runs a medical facility and a clinic offering comprehensive basic and emergency healthcare, as well as inpatient and laboratory services to Rohingya refugees and the local community. In response to the influx of refugees MSF has significantly increased water, sanitation and medical activities for the refugee population.
Elsewhere in Bangladesh, MSF works in Kamrangirchar slum, in the capital, Dhaka, providing mental health, reproductive healthcare, family planning and antenatal consultations, as well as an occupational health programme for factory workers.






